Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 Key Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education), Department of Physics and Astronomy, and Collaborative Innovation Center of IFSA (CICIFSA), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
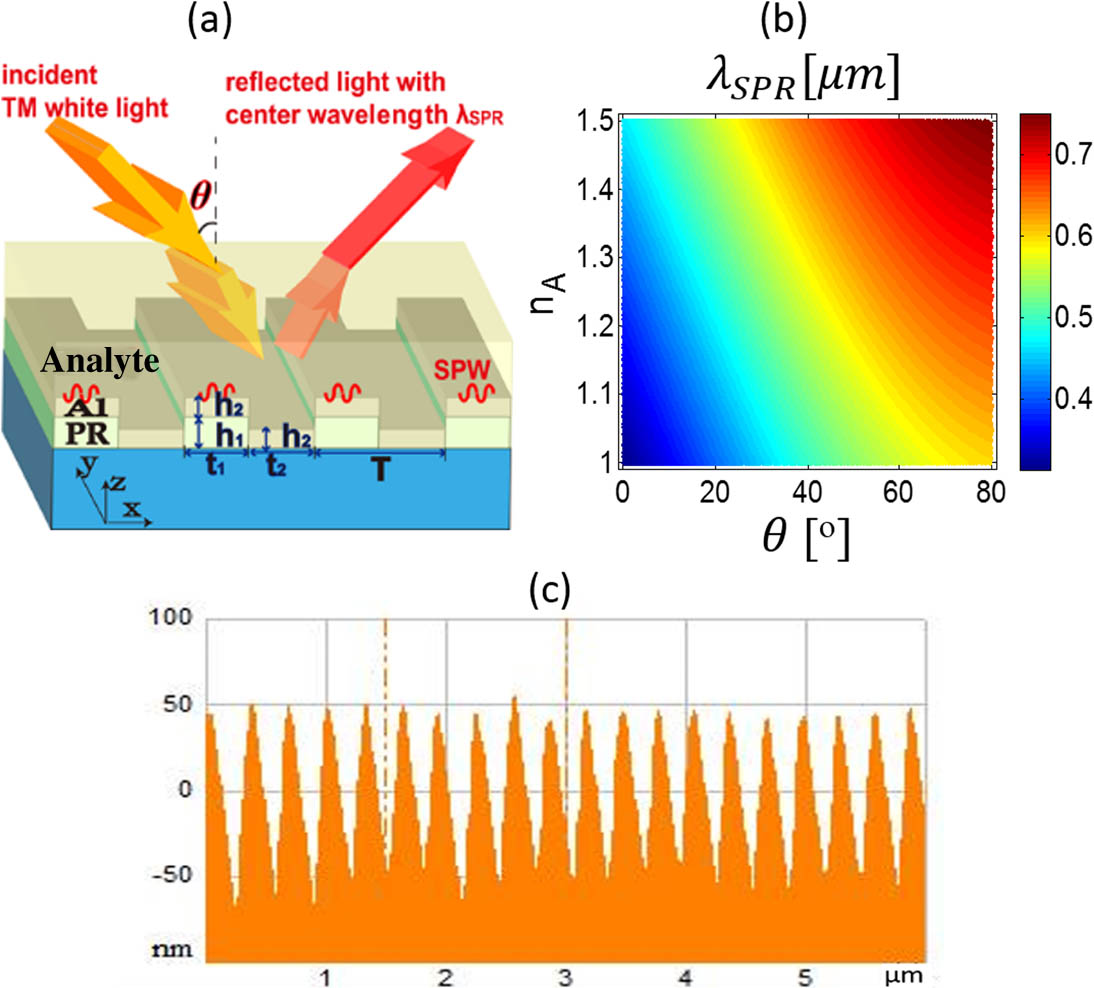
A grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance sensor based on bilayer aluminum nanowire arrays is fabricated by laser interference lithography. The device presents impressive reflective sharp peaks by lateral surface plasmon resonances even for aluminum thicknesses of merely several nanometers. Distinct reflective peaks and dramatic color shifts under different analytes are observed within a wide range of incident angle, metal thickness, and refractive index. The sensitivity of 307 nm per refractive index unit is experimentally obtained. The reflective-peak-type surface plasmon resonance sensors are suitable for practical applications because of easy fabrication, low cost, wide range, and high signal visibility.
surface plasmons subwavelength structure nanostructures sensor Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(5): 052401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (MoE) and School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of IFSA (CICIFSA), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
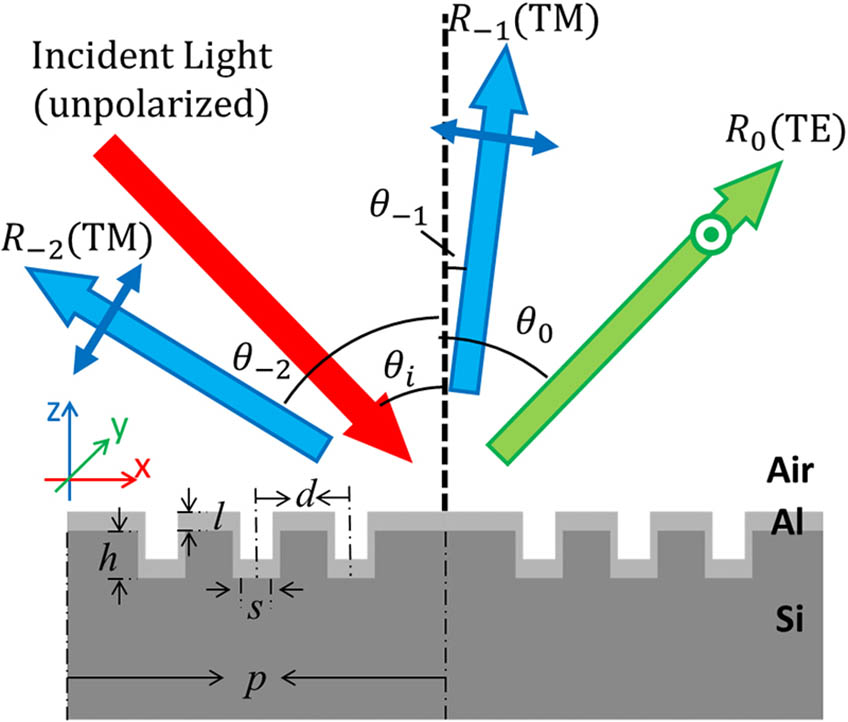
Separating lights into different paths according to the polarization states while keeping their respective path’s polarizations with high purification is keen for polarization multiplex in optical communications. Metallic nanowire gratings with multi-slits in a period are proposed to achieve polarized beam splitters (PBSs) in reflection and diffraction. The setting of multi-slits largely reduces the reflection of photons with a transverse magnetific field via the plasmonic waveguiding effect, which leads to highly polarized output lights with extinction ratio larger than 20 dB in each channel. The proposed reflection/diffraction PBSs enrich the approaches to control the polarization states with the advantages of wide incident angles and flexible beam splitting angles.
230.1360 Beam splitters 240.6680 Surface plasmons 230.1950 Diffraction gratings 060.4230 Multiplexing Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 052303
1 上海交通大学电子工程系TFT-LCD 关键材料及技术国家工程实验室, 上海 200240
2 昆山龙腾光电有限公司, 江苏 昆山 215300
纳米金属光栅上的表面等离子体共振(SPR)对临近材料折射率变化敏感,因此通过改变临近材料折射率,可以实现纳米金属光栅透射光谱的颜色调制进而用于显示器件,该调制器具有结构简单、色度和对比度高等特点。通过仿真设计实现了红绿蓝三个子像素的透射彩色显示。实验制备了周期为520 nm、铝厚度为50 nm 的双层金属光栅,并通过改变光栅临近材料折射率,实现了空气中为绿色亮态显示、蔗糖溶液中为暗态显示的效果,明暗对比度达到122。从理论和实验两方面证明了基于金属光栅结构的彩色显示和亮度调节的可行性,为未来电浸润显示器件提供了新的设计方案。
视觉光学 表面等离子体共振 纳米金属光栅 折射率 透射式显示 电浸润 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(4): 043301
1 上海交通大学 电子系, 上海 200240
2 昆山龙腾光电有限公司, 江苏 昆山215300
纳米金属光栅的透射光谱对临近材料折射率变化非常敏感, 可以通过改变介质折射率实现可调的彩色滤光, 将双层纳米金属光栅应用于显示装置上具有工艺制备简单、色度和对比度高等特点。采用纳米金属光栅结构, 通过严格耦合波理论模拟和表面等离子体共振原理设计了一种新型的透射式电润湿显示器件。在650nm周期、空气环境下, 通过数值优化在690nm波长处得到了50%的单色透射,而在水溶液的环境下, 由于共振移动到红外, 可以实现黑态显示, 从而验证了灰度的可调。该研究将为轻薄、节能和高分辨率的新型电浸润显示器件设计提供全新思路。
电润湿 表面等离子 纳米光栅 electrowetting surface plasmon resonance metallic nanowire gratings
1 装甲兵工程学院基础部, 北京 100072
2 上海交通大学电子工程系, 上海 200240
研究了亚波长光栅的衍射对抗反射和增强透射性能的影响。理论分析表明,如果要达到抗反射和增强透射的双重效果,需要避免衍射引起的横向波导损耗,光栅周期要足够小;而如果只需要达到抗反射效果,可利用光栅衍射形成横向波导共振降低反射效率,此时光栅周期不需要很小。利用严格耦合波理论对周期、占空比及凹槽深度等结构参数进行优化。采用激光干涉光刻法制作了周期为290 nm的一维浮雕光栅,并测试其透射及反射光谱,结果表明这种结构在大角度范围内对可见光波段有明显的抗反射效果,但是只有波长在非衍射区才具有透射增强效果,而在衍射区透射降低。该研究实验和理论分析相一致,研究结果为根据应用要求合理选择光栅周期、降低制备工艺提供了清晰的物理图像和参考。
光栅 亚波长光栅 衍射 抗反射 增透 波导共振
1 上海交通大学电子信息与电气工程学院电子系, 上海 200240
2 昆山龙腾光电有限公司, 江苏 昆山 215300
针对现有的量子点薄膜液晶显示背光技术中存在的材料利用率低和光学效率不高的缺点,提出了直接在导光板上制备量子点微结构的方法。新的背光架构由蓝光发光二极管(LED)激发量子点形成高显色性的白光。根据搭建显示背光系统模型,研究光线追踪的仿真模拟和光学参数优化,证明新结构的量子点背光具有高出光效率和低成本的优点。实验与理论结果相一致。
光学设计 微结构导光板 光线追踪 量子点 激光与光电子学进展
2015, 52(2): 022201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We demonstrate by finite-difference time-domain simulations that a one-dimensional (1D) photonic crystal (PC) structure between glass substrate and indium tin oxide layer can improve the light extraction efficiency of organic light-emitting diodes. The extraction efficiency depends on the emitters' positions varying laterally in a unit cell of PC. The highest efficiency is obtained when the emitters are under higher refractive index strips. Efficiency decreases when the emitters shift to lower refractive index strips. Simulations for both transverse magnetic and transverse electric modes indicate that when emitters are close to the middle of the higher refractive index strips, the guided wave transmits with less divergence and inhibited reflection because of the guiding effect of higher refractive index strips. A modified method that considers the position effects is proposed to calculate the extraction efficiency more precisely.
230.0230 Optical devices 230.7370 Waveguides 160.5298 Photonic crystals 160.4890 Organic materials 050.5298 Photonic crystals 310.2790 Guided waves Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(6): 062302





